Showing posts with label door. Show all posts
Showing posts with label door. Show all posts
Friday, September 5, 2014
Electronic Security Door Key Circuit Diagram
A different Electronic Security Door Key Circuit Diagram of electronic lock very simple, one and does not need a lot of materials in order to it is manufactured. The right keys of code should be stepped with the right line, so that is activated the optocupler IC2. If from error is stepped switch that does not belong in the combination, then the lock is trapped. In order to we restore the regular operation of lock, it should we press switches S1 or S12.
Read : Heat Detector Alarm using UM3561
Electronic Security Door Key Circuit Diagram
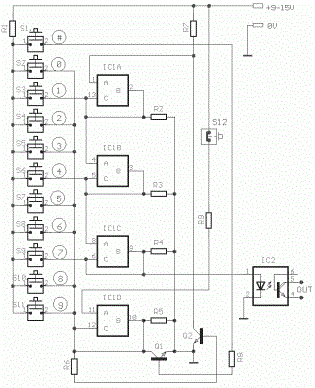
Switch S1 makes Reset of lock externally and the S12 internally, the door. The Code the circuit as he is connected it is 147 and it can change, very easily, changing the connections in the switches of keyboard. The optocupler IC2, can drive any exterior circuit as Relay etc, ensuring simultaneously electric isolation the two circuits. The circuit can be also supplied from a battery 9V.
Read : Radio Wave Alarm
Part List
R1-7-9=1Kohm
R2-3-4-5=100Kohm
R6 =10Kohm
R9 =47Kohm
IC1 = 4066
IC2 =4N25
Q1-2=BC550
S1...11=Push button sw or keyboard
S12=Push button normal closed
All resistors is 1/4W 5%
Tuesday, October 8, 2013
Laser Guided Door Opener
This automatic door opener can be made using readily available components. The electromagnetic relay at the output of this gadget can be used to control the DC/AC door-opener motor/solenoid of an electromechanical door opener assembly, with slight intervention in its electrical wiring. A laser diode (LED1) is used here as the light transmitter. Alternatively, you can use any available laser pointer. The combination of resistor R1 and diode D1 protects the laser diode from over-current flow. By varying multi-turn trimpot VR1, you can adjust the sensitivity. (Note that ambient light reflections may slightly degrade the performance of this unit.) Initially, when the laser beam is falling on photo-transistor T1, it conducts to reverse-bias transistor T3 and the input to the first gate (N1) of IC1 (CD4001) is low.
The high output at pin 3 of gate N1 forward biases the LED-driver transistor (T4) and the green standby LED (LED2) lights up continuously. The rest of the circuit remains in standby state. When someone interrupts the laser beam, photo-transistor T1 stops conducting and transistor T3 becomes forward-biased. This makes the output of gate N1 go low. Thus LED-driver transistor T4 becomes reverse-biased and LED2 stops glowing. At the same time, the low output of gate N1 makes the output of N2 high. Instantly, this high level at pin 4 of gate N2 triggers the monostable multivibrator built around the remaining two gates of IC1 (N3 and N4). Values of resistor R8 and capacitor C1 determine the time period of the monostable.
 The second monostable built around IC2 (CD4538) is enabled by the high-going pulse at its input pin 12 through the output of gate N4 of the first monostable when the laser beam is interrupted. As a result, relay RL1 energizes and the door-opener motor starts operating. LED3 glows to indicate that the door-opener motor is getting the supply. At the same time, piezo-buzzer PZ1 sounds an alert. Transistor T5, whose base is connected to Q output (pin 10) of IC2, is used for driving the relay. Transistor T6, whose base is connected to Q output of IC2, is used for driving the intermittent piezo-buzzer. ‘On’ time of relay RL1 can be adjusted by varying trimpot VR2. Resistor R9, variable resistor VR2 and capacitor C3 decide the time period of the second monostable and through it on time of RL1.
The second monostable built around IC2 (CD4538) is enabled by the high-going pulse at its input pin 12 through the output of gate N4 of the first monostable when the laser beam is interrupted. As a result, relay RL1 energizes and the door-opener motor starts operating. LED3 glows to indicate that the door-opener motor is getting the supply. At the same time, piezo-buzzer PZ1 sounds an alert. Transistor T5, whose base is connected to Q output (pin 10) of IC2, is used for driving the relay. Transistor T6, whose base is connected to Q output of IC2, is used for driving the intermittent piezo-buzzer. ‘On’ time of relay RL1 can be adjusted by varying trimpot VR2. Resistor R9, variable resistor VR2 and capacitor C3 decide the time period of the second monostable and through it on time of RL1.
The circuit works off 12V DC power supply. Assemble it on a general-purpose PCB. After construction, mount the laser diode and the photo-transistor on opposite sides of the door-frame and align them such that the light beam from the laser diode falls on the photo-transistor directly. The motor connected to the pole of relay contacts is the one used in electromechanical door-opener assembly. If you want to use a DC motor, replace mains AC connection with a DC power supply.
Readmore...
The high output at pin 3 of gate N1 forward biases the LED-driver transistor (T4) and the green standby LED (LED2) lights up continuously. The rest of the circuit remains in standby state. When someone interrupts the laser beam, photo-transistor T1 stops conducting and transistor T3 becomes forward-biased. This makes the output of gate N1 go low. Thus LED-driver transistor T4 becomes reverse-biased and LED2 stops glowing. At the same time, the low output of gate N1 makes the output of N2 high. Instantly, this high level at pin 4 of gate N2 triggers the monostable multivibrator built around the remaining two gates of IC1 (N3 and N4). Values of resistor R8 and capacitor C1 determine the time period of the monostable.
 The second monostable built around IC2 (CD4538) is enabled by the high-going pulse at its input pin 12 through the output of gate N4 of the first monostable when the laser beam is interrupted. As a result, relay RL1 energizes and the door-opener motor starts operating. LED3 glows to indicate that the door-opener motor is getting the supply. At the same time, piezo-buzzer PZ1 sounds an alert. Transistor T5, whose base is connected to Q output (pin 10) of IC2, is used for driving the relay. Transistor T6, whose base is connected to Q output of IC2, is used for driving the intermittent piezo-buzzer. ‘On’ time of relay RL1 can be adjusted by varying trimpot VR2. Resistor R9, variable resistor VR2 and capacitor C3 decide the time period of the second monostable and through it on time of RL1.
The second monostable built around IC2 (CD4538) is enabled by the high-going pulse at its input pin 12 through the output of gate N4 of the first monostable when the laser beam is interrupted. As a result, relay RL1 energizes and the door-opener motor starts operating. LED3 glows to indicate that the door-opener motor is getting the supply. At the same time, piezo-buzzer PZ1 sounds an alert. Transistor T5, whose base is connected to Q output (pin 10) of IC2, is used for driving the relay. Transistor T6, whose base is connected to Q output of IC2, is used for driving the intermittent piezo-buzzer. ‘On’ time of relay RL1 can be adjusted by varying trimpot VR2. Resistor R9, variable resistor VR2 and capacitor C3 decide the time period of the second monostable and through it on time of RL1.The circuit works off 12V DC power supply. Assemble it on a general-purpose PCB. After construction, mount the laser diode and the photo-transistor on opposite sides of the door-frame and align them such that the light beam from the laser diode falls on the photo-transistor directly. The motor connected to the pole of relay contacts is the one used in electromechanical door-opener assembly. If you want to use a DC motor, replace mains AC connection with a DC power supply.
Subscribe to:
Posts (Atom)